Within the current regulatory framework, specific provisions have been incorporated that directly affect the rights and benefits applicable to people with disabilities, their substitutes, and caregivers, as well as those facing rare, orphan, catastrophic, or complex diseases. These reforms cover key aspects related to access to services, labor, education, and health benefits. We highlight the following:
- Person with Disability: An individual presenting structural or functional, bodily, mental, intellectual, sensory, or psychosocial impairments and limitations in exercising essential daily life activities autonomously.
The Law introduces a new category of disability not regulated in the previous statute, namely psychosocial impairments.
Previously, applicable regulations determined that the rights of people with disabilities depended on their disability percentage. However, the current law eliminated this classification system, proposing instead that disability be categorized as mild, moderate, severe, very severe, and complete.
- Direct Substitute: A person responsible for the maintenance or care of individuals with severe, very severe, or complete disabilities, related up to the fourth degree of consanguinity and the second degree of affinity.
Parents and legal representatives of minors with any type and percentage of disability are also considered direct substitutes.
Certification of Direct Substitutes:
- People seeking recognition as substitutes for adults with severe, very severe, or complete disabilities must submit a certificate of non-affiliation to the social security under a dependency regime.
- Where certification of substitute status is required by an employer to comply with inclusion quotas, a copy of the employment contract must be submitted.
- People with disabilities may, if deemed necessary, request the withdrawal of substitute status.
- Employers are required to register within 30 days, in the system established by the Ministry of Labor, those employees who have notified them of their substitute status.
- Failure to register may result in a fine of USD 200 per unregistered employee, up to a maximum of 20 Unified Basic Salaries (currently USD 9,400.00).
- Employees are likewise obligated to notify their employer of their substitute status.
- The Ministry of Labor, through the SUT platform, has implemented a complementary system to verify the authenticity of substitute certificates.
- Caregiver: The new law introduces the category of caregiver, defined as the mother, father, legal representative, or guardian authorized to care for a person with a severe, very severe, or complete disability.
Caregivers assume responsibility for assisting people with disabilities who, to varying degrees, require support in carrying out daily life activities.
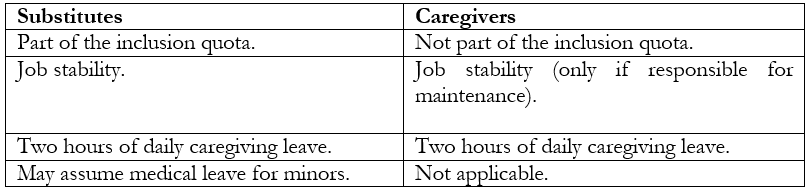
This role confers rights distinct from those of substitutes, and caregivers are not included within the inclusion quota.
- Remote Work Authorization: people with disabilities pursuing postgraduate or continued education systems can request to work remotely.
- Labor Inclusion: employers with 25 or more employees must include at least 4% of people with disabilities. Substitute personnel may be included within the quota, provided they do not exceed 25% of the total inclusion required.
To fully comply with the quota, employers must apply principles of gender equity and disability diversity, and where operations exist in multiple provinces, distribute included personnel equitably.
Noncompliance may result in monetary sanctions of 11 to 15 unified basic salaries or the suspension of activities for up to thirty days.
- Labor Inclusion for Private Security Companies: for the purpose of calculating the inclusion quota, private security and surveillance companies may consider substitutes in operational roles, even exceeding the maximum percentage allowed in other sectors.
- Employment Conditions: people with disabilities must be hired on full-time schedules (8 hours), under contractual modalities deemed stable or permanent by law.
Part-time employment is permitted only with medical certification confirming the impossibility of full-time work.
- Job Stability: people with disabilities, as well as those responsible for their maintenance and/or care, enjoy reinforced job stability. Unjustified dismissal entitles them to either reinstatement or additional severance equal to 18 months of the highest salary received from the employer.
- Extended Maternity Leave: in cases of childbirth involving minors with disabilities or severe congenital conditions, maternity leave is extended by three months.
- Leave for Substitutes and Caregivers: individuals responsible for people with severe, very severe, or complete disabilities are entitled to two hours of daily leave for caregiving purposes.
- People with Rare, Orphan, Catastrophic, or Highly Complex Diseases Employment Rights: employees who demonstrate such conditions are entitled to workplace accommodations, including modified schedules, where necessary.
- Rights of Substitutes and Caregivers:
13. Income Tax Deduction: employers may deduct an additional 150% of all remunerations and benefits contributed to social security (IESS) with respect to disabled employees and substitutes exceeding the mandatory inclusion quota.
14. Tax Exempt from Vehicle Imports: In the case of used vehicles, the model must correspond to the last three years prior to importation, (between the model year and the year of shipment).
The beneficiary may access a new tax-exempt importation five years after the Customs Import Declaration has been cleared.
15. Local Purchase of Exempt Vehicles: local purchase must be authorized by the Internal Revenue Service within a maximum period of 30 days from the submission of the application. Only new vehicles will be exempt from local taxes. The beneficiary may access a new exemption five years after the local purchase.
If it is determined that the conditions for benefiting from the exemption on local vehicle purchases were not met, the Internal Revenue Service will recalculate the tax for the total amount of the exempted values plus the respective interest.
16. Exceptional Transfer Clause: if the person with a disability benefiting from the tax exemption is unable to fulfill their financial obligation to the seller of the vehicle due to an emerging personal economic crisis, they may request the transfer of the vehicle within one year from the date of importation or acquisition.
To this end, the person with a disability or the person interested in acquiring the vehicle, duly authorized by the beneficiary of the exemption, may request the transfer of ownership of the vehicle from the customs or tax authority, as appropriate, and pay the proportional part of the taxes remaining to complete the five-year period, calculated from the date of submission of the transfer request.
To this end, the person with a disability must, by means of a sworn statement before a notary public, justify the reasons for their emerging financial hardship; they will be prevented from benefiting from this exemption again until five years have elapsed from the date of release of the import or acquisition, as applicable.
17. Use of Exempt Vehicles: vehicles imported or purchased locally with tax exemption must be driven by the person with a disability who is the beneficiary of the exemption. Extraordinarily, and depending on the condition of the person with a disability, the vehicle may be driven by:
- Members of the family unit of the person with a disability, including up to the second degree of consanguinity and first degree of affinity.
- A person outside the immediate family, if they can prove that the person with a disability is under their protection, care, or dependency (e.g., driver) and that the person with a disability is in the vehicle.
- In emergency situations, when the person with a disability is unable to drive the vehicle due to exceptional circumstances, duly justified and verifiable if applicable.
**Legal References:
- Organic Law for Persons with Disabilities. Published July 3, 2025, Fourth Supplement of the Official Gazette No. 73.
- Ministerial Agreement MDT-2025-105 “Regulation for the Certification of Direct Substitutes of Persons with Disabilities.” Published August 26, 2025, Third Supplement of the Official Gazette No. 110.
- Organic Reform Law to Various Legal Bodies to Guarantee the Labor Rights of Persons with Disabilities, Rare, Orphan, Catastrophic, and Highly Complex Diseases, and Their Substitutes. Published June 20, 2025, Fifth Supplement of the Official Gazette No. 64.

Andrea Moya, Partner at CorralRosales
amoya@corralrosales.com
+593 2 2544144

Edmundo Ramos, partner at CorralRosales
eramos@corralrosales.com
+593 2 2544144














